A hip click can be felt by the examiner when the hip joints may not have formed normally. How is hip dysplasia treated in babies.

Leerburg The Importance Of Good Positioning On Canine Hip X Rays Canine X Ray Hips
They give your healthcare provider information about structures inside the body.

. It has nothing to do with whether or not the parents will hold the infant. Once the radiographer a person specially trained in taking X-ray images has positioned the part of your childs body to be examined and lined up the X-ray machine the X-ray examination takes less than a second to perform. Inflammation where your sacrum joins.
X-rays can be taken once your baby is 3 months old. At birth the baby cant move the thigh outward at the hip as far as normally possible. The doctor first checks your babys hips in the hospital after birth.
They do this by gently pushing and pulling the babys thigh bones to see if they are loose in the hip socket. X-rays can be taken once your baby is 3 months old. They can penetrate your body.
Risk factors include 14. Appointments and Referrals. But for babies with an abnormal physical exam or major risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip or DDH family history Breech position etc the AAP supports referral for.
The frog leg lateral view is a special radiograph of the pelvis to evaluate the hip. They are of more concern. It occurs more commonly in boys typically between 5 and 8 years of age but may range from the ages 3-12.
The American Academy of Pediatrics does not recommend routine ultrasounds for every infant. The doctor hears or feels a hip click when moving the infants thigh outward. Perthes disease also known as Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is an idiopathic avascular necrosis of the proximal femoral epiphysis.
However x-rays of the mothers lower torso - abdomen stomach pelvis lower back or kidneys - may expose the unborn child to the direct x-ray beam. After around 4 to 6 months of age X-rays are the preferred method for evaluating and monitoring hip dysplasia. X-rays are forms of radiant energy like light or radio waves.
Two tests are performed called the Barlow and Ortolani tests to examine the function of the hip joints. Whilst the parent puts on a lead gown it is the radiographers responsibility to ensure the baby does not roll off the x-ray table. Hip X-rays are done with a child lying on a table.
Because of the risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants born breech-despite a normal physical exam-the American Academy of Pediatrics AAP guidelines recommend ultrasound US hip imaging at 6 weeks of age for breech females and optional imaging for breech males. Is extremely beneficial for pelvis imaging as young children will often begin to cry the moment they are placed supine. Hip problems may not be present at birth.
An X-ray technician will take pictures of the hip. If a physical exam an ultrasound or an X-ray confirm a diagnosis your pediatrician will likely refer you to a pediatric orthopedic specialist for continued care and treatment. The reported incidence of developmental dysplasia of the hip varies between 15 and 20 per 1000 births 1 with the majority 60-80 of abnormal hips resolving spontaneously within 2-8 weeks 1 so-called immature hip.
You will go in the room with him he will need to be stripped from the waist down they will take x-rays of him flat on his back legs dead straight and together you wil be able to hold him in this position then an x-ray of his still on his back with his knees bent facing outwards and the soles of his feet put together he will be fine. Arthritis that affects your hip. X-ray examinations are usually quick and simple.
Subsequent x-rays will track the hip joints progress. Your baby was born in the breech position after 28 weeks of. From the front anteroposterior view or AP from the side lateral view also known as the frog leg lateral view Typically X-rays of both hips are taken for comparison even if only one hip is causing symptoms.
Hip ultrasounds take less than 20 minutes and the child will not feel any pain during the examination. X-rays have more energy than rays of visible light or radio waves. Most children do not need surgery but for those who do an arthrogram x-ray dye injected into the hip joint at the beginning of the surgery can help the surgeon decide exactly what needs to be corrected.
In addition exposing the parents to ionizing radiation X-rays needlessly goes against the ALARA principle. After around 4 to 6 months of age X-rays are the preferred method for evaluating and monitoring hip dysplasia. A type IIa- hip is at risk to develop dysplasia.
Pregnancy is a time to take good care of yourself and your unborn child. X-rays are a kind of imaging test. If it persists they may put on a spica cast.
A hip ultrasound might be done for a baby if the doctor finds a hip problem such as. Its a cast that goes around both hips and down the leg to keep the hips aligned. A pelvic X-ray can help your doctor detect various conditions such as.
During treatment x-rays can reveal the progress of the hip as it improves. Then a surgeon gently pushes the ball of their thighbone joint into the hip socket where it belongs. An ultrasound may be needed to get a picture of the hip.
These tests expose children to low doses of radiation. If she does have it they may try to brace it first. Ultrasounds use inaudible sound waves which bounce off of the bones and muscles to create an image for radiologists to interpret.
So an alpha angle of 56 degrees at the age of 7 weeks is called type IIa while at the age of 10 weeks it is called a type IIa-. F ratio 18 firstborn baby. It is put on by an orthopedic surgeon while using.
They may become an issue as your. It can occur bilaterally but it is usually asymmetric. If a child is older than 3 months or 13 weeks then an alpha angle of 50-59 degrees is considered a sign of dysplasia ie type IIb.
Your child may be required to hold his or her breath or remain still. The purpose of this study is to report US results and follow-up of. Hip ultrasounds are a safe non-invasive procedure that does not use any radiation.
In babies with hip dysplasia the joint has not formed normally and the hips are prone to moving in and out of joint. What Are the.

Perthes Ds X Ray Femoral Head Necrosis Disease Skull Calves

Pin On Adult Hip Dysplasia Awareness

My Hips Pre Pao Rpao January 2011 Rpao January 2011 Screws From My Rpao X Ray Ehlers Danlos Syndrome Surgery Recovery

Uk Professor Says Swaddling Epidemic Gives Babies Clicky Hips Daily Mail Online Hips Professor Baby Swaddle

Diagnosis Prevention And Management Of Canine Hip Dysplasia A Revie Vmrr Canine Hip Dysplasia Diagnostic Imaging Total Hip Replacement

Severe Hip Dysplasia In A Boxer The Red Arrows Are Pointing To The Over Growth Of Bone At The Femoral Neck Head The Red Arrow Shades Of Grey Hip Dysplasia

Canine Ofa Hip Xrays Goldendoodle Puppy For Sale Labradoodle Goldendoodle Goldendoodle Puppy

Lower Limb Radiographs Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Sacroiliac Joint

Causes Of Ddh Hip Dysplasia Baby Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Baby Wearing
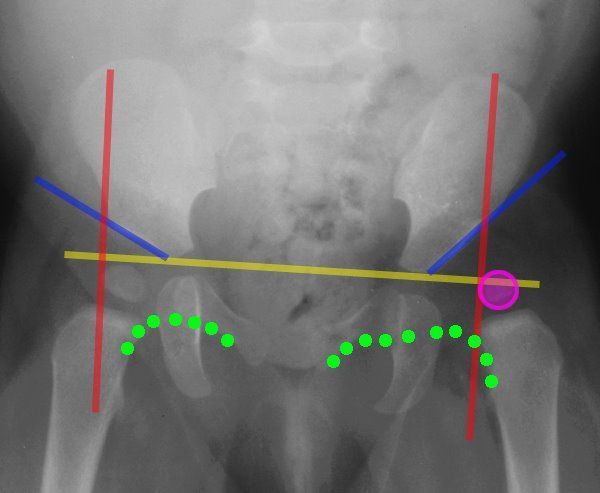
Lines Of The Hip Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Radiology

Basic Information About Dog Hip Dysplasia Paperblog Dog Hip Dysplasia Hip Dysplasia Canine Hip Dysplasia

Pin On Fibro Autoimmune Diseases

Pin By Meg Carter On Ortho Hip Dysplasia X Ray Orthopedics

Congenital Hip Dislocation Chd Happens When A Child Is Born With An Unstable Hip Read On To Learn More Ab Canine Hip Dysplasia Hip Dysplasia Hip Dislocation

Anatomy Pathology Medicine Nursing Radiography Radiologictechnologist Radiology Radiologystudent Instagram Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Radiology

How To Shower After Hip Replacement Surgery Livestrong Com Hip Replacement Surgery Hip Replacement Exercises Hip Brace

X Ray Image Of Child Swallowed The Coins For A Medical Diagnosis Medicine Pictures Children Images X Ray Images


